The Council on Library and Information Resources has awarded one of its Digitizing Hidden Collections grants to the Philadelphia Area Consortium of Special Collections Libraries (PACSCL). It will support digitization of virtually all the medieval manuscripts in PACSCL member collections and to place them in a common repository with previously digitized manuscripts as free cultural works. The project, “Bibliotheca Philadelphiensis: Toward A Comprehensive Online Library of Medieval and Early Modern Manuscripts in PACSCL Libraries in Eastern Pennsylvania and Delaware,” includes manuscripts from Lehigh University; Free Library of Philadelphia; University of Pennsylvania Libraries; Bryn Mawr College; College of Physicians of Philadelphia; Haverford College; Library Company of Philadelphia; Rosenbach Museum and Library; Swarthmore College; Temple University; University of Delaware; Chemical Heritage Foundation; Franklin & Marshall College; Villanova University; and the Philadelphia Museum of Art.
The proposal funded by CLIR describes the value of the project: “This project will provide online access to high-resolution images, with metadata, of 159,512 pages of medieval manuscripts from more than 400 codices plus leaves. These images will be released to the public domain for free use by scholars and the general public and, added to existing digitized resources, will make the overwhelming majority of the region’s medieval manuscripts–one of the largest concentrations in the United States–available worldwide, in their entirety and easily downloadable. By providing unfettered, unmediated consolidated access to such a comprehensive corpus of images and metadata, the project will shape a new understanding of libraries’ and archives’ role in sharing our historical and cultural heritage.”
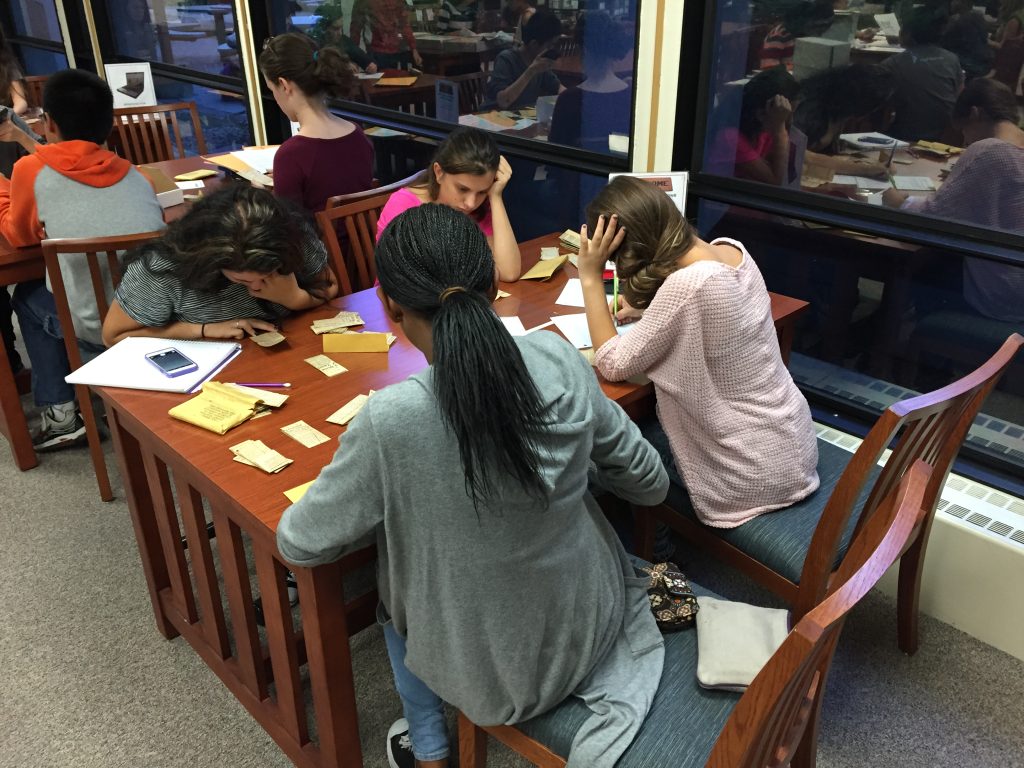
Temple students use the medieval manuscripts in Temple’s Special Collections Research Center to study the history of the book, illustration, printing techniques, and ancient texts, and to grow in primary source literacy and evaluation of resources. The texts also serve as inspiration for the students’ own creative projects. While the manuscripts already support teaching in multiple disciplines, in their digital form they will expand opportunities for study and digital scholarship. Temple’s holdings are particularly strong in legal and business history, but also include a late 15th century French illuminated Book of Hours, other religious texts, and music.
–Margery Sly, Director, Special Collections