The Special Collections Research Center is pleased to announce the Jewish Community Relations Council of Greater Philadelphia Records are now open for research use. The JCRC records were donated to the Philadelphia Jewish Archives Center between 1976 and 2006 and acquired by the Special Collections Research Center in June 2009 where they were the focus of a two-year processing project. View the online finding aid or guide to the collection on the Libraries’ website.
The Special Collections Research Center is pleased to announce the Jewish Community Relations Council of Greater Philadelphia Records are now open for research use. The JCRC records were donated to the Philadelphia Jewish Archives Center between 1976 and 2006 and acquired by the Special Collections Research Center in June 2009 where they were the focus of a two-year processing project. View the online finding aid or guide to the collection on the Libraries’ website.
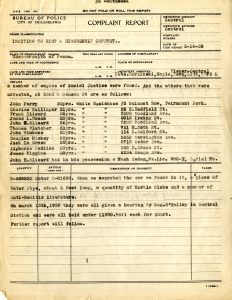
The Jewish Community Relations Council of Greater Philadelphia (JCRC) was founded on January 30, 1939, as the Anti-Defamation Council but changed their name in 1943. The impetus for the formation of the JCRC was the rise of antisemitism in America after fascism took hold of much of Europe in the late 1930s. Jewish community leaders perceived the need for a unified voice dedicated specifically to fighting antisemitism and protecting the rights of the Jewish Community in Philadelphia. The JCRC’s mission has traditionally been defined as “…helping members of all religious, racial and ethnic groups to work and live together democratically and cooperatively by equalizing their treatment, enlarging their opportunities and deepening their mutual appreciation.” The Jewish Community Relations Council is still in existence and works as a constituent agency of the Jewish Federation of Greater Philadelphia.
The bulk of the records span JCRC history from its founding in 1939 through the mid-1990s. Subject strengths include the struggle against antisemitism and racism in any form, including violence, vandalism, and propaganda, or in any aspect of society, such as education, employment, and housing. Other well-documented subjects include prayer in schools, interreligious relations, the relationship between the black and Jewish communities, Holocaust remembrance, Soviet Jewry, and the state of Israel.

Of particular interest are data, surveys, and compiled reports on the admissions practices of Philadelphia’s professional schools in the 1940s.
Also noteworthy are records pertaining to the Black-Jewish Loan Fund, a JCRC–created program which offered low or no interest loans to members of the black community interested in purchasing Jewish-owned business in neighborhoods of shifting demographics.
— Casey Babcock, Project Archivist, SCRC