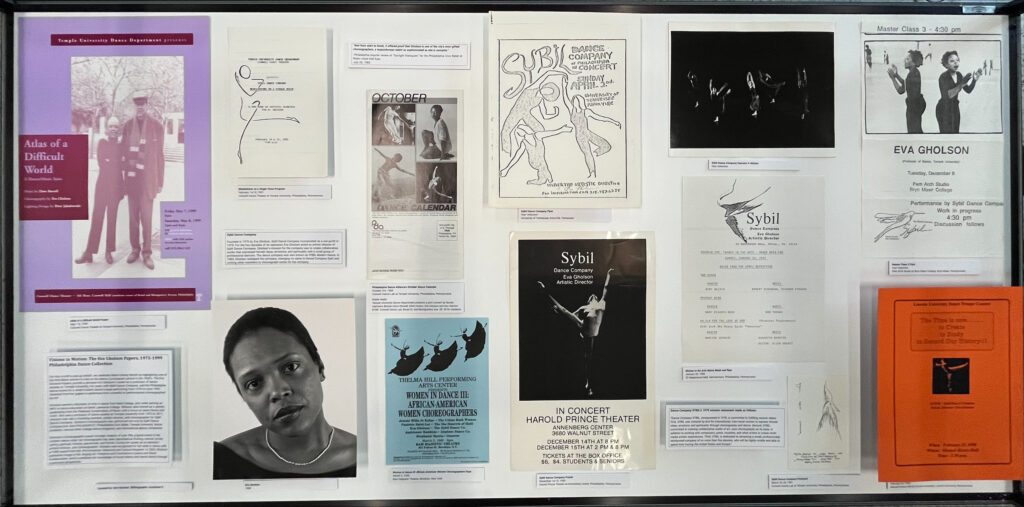
This month’s pop-up exhibit in the SCRC Reading Room recognizes Black History Month by highlighting the Papers of Eva Gholson, the first Black women to train at the Merce Cunningham studio in the 1960’s. The Eva Gholson Papers provide a glimpse into Gholson’s career as a professor of dance studies at Temple University, her years with Sybil Dance Company, and the Philadelphia dance scene for a small modern dance troupe during the mid-1970s to the early-1990s.
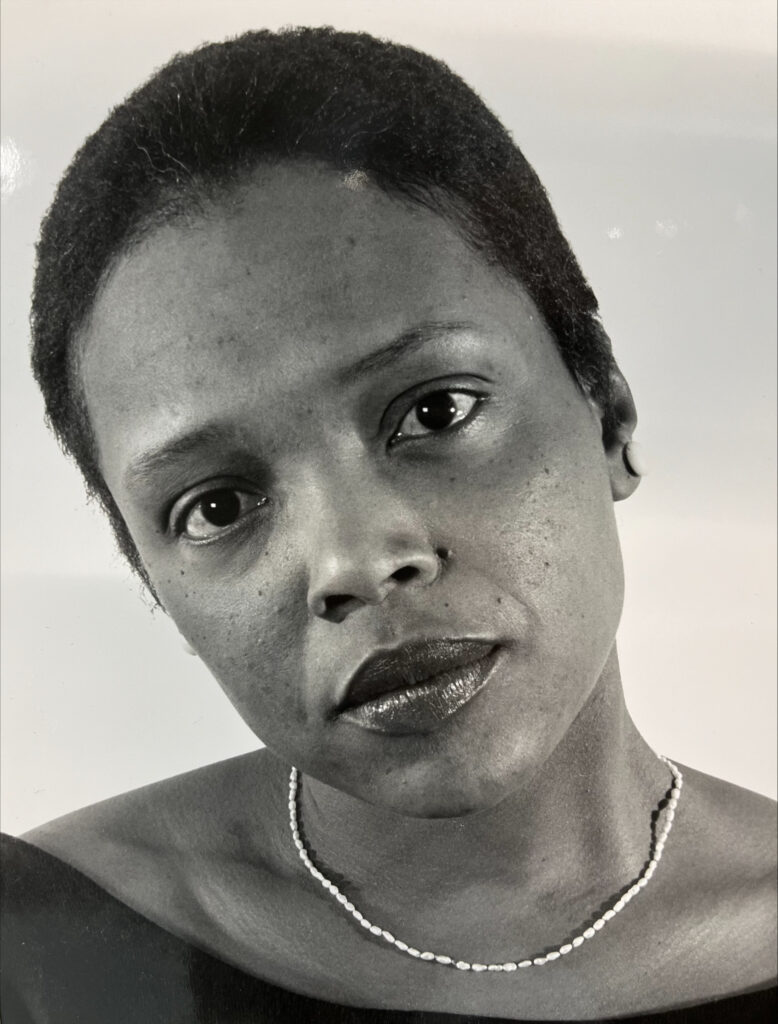

Gholson earned a Bachelor of Arts in dance from Bard College and an MFA in dance education at Sarah Lawrence College. Gholson also trained as a pianist, graduating from the Peabody Conservatory of Music with a focus on piano theory and violin. She was a professor of dance studies at Temple University from 1972 to 2011. Gholson was also a founding member, artistic director, and choreographer for Sybil Dance Company. Gholson’s choreography was performed not only by Sybil Dance Company but also PHILADANCO!, Philadelphia Civic Ballet, Temple University dance students, various other college dance programs dance companies around the world.

During her career in choreography Gholson created over fifty original works in the modern dance style. Her choreography has been described by various critics as flowing, natural, lyrical, earthy, spiritual, intense, passionate, and formal. As an educator, artistic director, and choreographer, Gholson was recognized for her work in dance with a 1988 award from the Afro-American Historical and Cultural Museum. In 2004, Gholson published Image of the Singing Air: Presence and Conscience in Dance and Music Collaboration, which combined her personal perspective with her knowledge of music and dance theory.
A selection of ephemera from performances Gholson choreographed is on display in the SCRC Reading room this month.