Another Look at Active Learning: Part 7: Overcoming Challenges to Active Learning
Another Look at Active Learning, Part 6: Active Learning Online, Synchronously and Asynchronously

by Emtinan Alqurashi, Ed. D
In our ongoing series, “Another Look at Active Learning,” we’ve explored various active learning techniques. While active learning is an effective approach in all types of courses, its application can differ in online environments. This is especially true for asynchronous courses where students lack real-time contact with the instructor and their peers. So it becomes crucial to establish opportunities for active engagement with the instructor and fellow students in asynchronous settings. In this blog post, we delve into activities that can effectively engage students in both synchronous and asynchronous online learning settings.
Synchronous active learning strategies
Synchronous activities take place in real-time, often using platforms like Zoom. They often mirror the types of activities that we use in in-person settings, with some adjustments to help them work in this modality.
Examples
Strategy #1: Jigsaw Online
How it works:
Step 1: Identify a reading or learning unit that can be divided into parts.
Step 2: Form small groups and have each group focus on one of the parts. This can be completed prior to class, or by reading independently during class time.
Step 3: In class, form breakout rooms for each group to allow them to discuss their part with the goal of being able to explain it to other classmates. They should be working together to identify key concepts and clarify any gaps in understanding. Then, have them return to the main room.
Step 4: Form new groups in the breakout room so that each new group has one member for each of the different parts. I recommend asking students to add their Step 3 breakout room number next to their names to make it easier for instructors to reform the groups. Each group member now explains their part to the other members in the new group.
Step 5: Optional: Provide the new groups with a problem to solve that requires the integration of the different parts.
Strategy #2: Rotating Stations
How it works:
Step 1: Define the learning unit and craft a set of open-ended discussion questions before class.
Step 2: Create shareable collaborative documents (e.g. Google Docs) for each question, and change the sharing setting to enable “edit access for anyone with a link”. Provide all the links on a single Google Doc, using it as the central hub.
Step 3: In class, establish breakout rooms for group discussions. Have students record their answers in the documents and rotate every 10 minutes through the questions.
Step 4: After they’ve cycled through all stations (i.e. google docs), bring them back to the main room for discussion through chat, raised hands, or taking turns to speak.
Note: Monitor document activity to support groups if needed during the activity.
Strategy #3: Digital Sticky Notes
Sticky notes are great for getting lots of student ideas quickly. You can use them for brainstorming together in real time, making mind maps, and helping students sort out concepts to boost their critical thinking.
Digital sticky notes work just like the real ones, they can be added by everyone, and you can keep coming back to them. Padlet is an easy digital sticky note tool to use, great for sharing and collaborative editing.
Strategy #4: Live Polling
Uses for live polling:
- Assess Learning: Use multiple-choice or open-ended polls to assess comprehension.
- Build Community: Foster a sense of belonging using image or word cloud polls.
- Gather Feedback: Collect course and teaching feedback.
- Facilitate Peer Learning: Encourage discussions and decision-making through polls.
Use Poll Everywhere for both in-person and online teaching; it integrates into presentations with various question types. Kahoot, another polling tool, enables creating multiple-choice questions for instant feedback and leaderboards. Employ Kahoot games for knowledge reinforcement, review, or as individual challenges for asynchronous learning with set deadlines.
Asynchronous active learning strategies
Asynchronous activities occur at students’ own pace and on their schedule. Designed well, they can be successful at actively engaging students with the content and with others in the class.
Examples
Strategy #1: Collaborative Writing
Consider using collaborative writing tools like Google Docs, or Microsoft Word, when assigning group writing projects where students can work together asynchronously. These tools are very useful because they allow everyone to contribute and edit the same documents. In addition, they have features like tracking changes and adding comments, which make it easy for everyone to give feedback and improve the work together.
Strategy #2: Peer Review
Leverage peer review for student connections and enhanced learning using Canvas Peer Review in asynchronous classes, and keep the following considerations in mind:
- Define expectations: Provide precise instructions for the criteria students should consider in their reviews.
- Offer guidance: Provide students with guiding questions, rubrics, or worksheets to assist them in their peer reviews. This can aid in structured and focused evaluations.
- Encourage author questions: Encourage students to include initial questions for their peer reviewers to guide them on what aspects the author would like them to focus on.
Strategy #3: Gamification, like Escape Games
Using gamification, like online escape games, is an exciting and effective approach to foster active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills among students. To create and manage such games, select a suitable tool (e.g., Genially), and design the game with a storyline, puzzles, and challenges aligned with the learning objectives. Provide clear instructions, establish support and feedback channels, and encourage engagement through debriefing discussions to review solutions and outcomes. It’s worth noting that escape games can be utilized synchronously where you give students a link to the game and then return to debrief.
Strategy # 4: Online Discussions
Using tools like VoiceThread for online discussions is excellent for engaging students, especially in asynchronous courses. VoiceThread is an interactive collaboration tool where you can share materials and multimedia, and students can add text, audio, or video comments directly. It facilitates rich discussions and allows students to interact directly with shared material and also build digital presentations with comments for discussion.
Strategy #5: Generative AI
Generative AI, like ChatGPT, offers exciting opportunities for engaging students in active learning. Refer to the CAT AI guide on how to incorporate these activities in our EDvice Exchange blog post A Survival Guide to AI and Teaching pt.4: Make AI Your Friend.
If you’re interested in trying these techniques, we encourage you to reach out to the CAT. In the next post of this blog series, we will focus on overcoming challenges in active learning.
Emtinan Alqurashi is Assistant Director of Online and Digital Learning at Temple’s Center for the Advancement of Teaching.
Another Look at Active Learning, part 5: Active Learning in Large Classrooms
Testing Assignments in ChatGPT
Another Look at Active Learning, Part 4: Long-term Active Learning Techniques
Dana Dawson, Ph.D. and Cliff Rouder, Ed.D.

In part 2 of our series on active learning, we identified high-impact, easy-to-implement active learning techniques, and in part 3, we explored peer and collaborative learning. In this part, we’re going to examine high-impact active learning techniques that extend beyond a single class period, possibly spanning an entire semester or even the entire year. These techniques require a bigger planning component and involve a significant shift in roles for the instructor and for students as students assume more responsibility for their own learning. However, they also yield big rewards, including deriving solutions to real-world problems, increased engagement and greater ability to communicate/work effectively in groups. So without further ado, let’s take a look at a variety of long-term active learning techniques.
Experiential Learning
Experiential learning encompasses activities that invite students to learn by doing. Students apply the skills and knowledge they’re learning in their courses within actual civic and work-based contexts that place them in a position to grapple with and reflect on real-world problems. This approach improves student engagement and retention because there are meaningful stakes involved and students can see how what they’re learning will be used in post-graduate situations.
Case-Based Learning
In case-based learning, students are presented with real-world scenarios and asked to apply their knowledge to come up with solutions or to advise on the best way to address the issue at hand. It is a form of guided inquiry where the problem is defined and students use knowledge and skills gained in the classroom to tackle the problem, or in some instances, choose from a set of possible solutions or analyze how others have resolved the scenario.
Project-Based Learning
In project-based learning, students are presented with a complex real-life scenario that has multiple potential solutions. Working in groups, students develop a plan and design and create a ‘hands-on-solution’ in the form of a product or artifact to address the problem.
Problem-Based Learning
Here, students are presented with a case or scenario where they define the problem, explore related issues, and identify a solution. While similar to case-based and project-based learning, problem-based learning is generally less structured and more open ended, and the problem is typically not as well defined as in case-based learning. Problem-based learning focuses on the process of discovery, with students working to define and solve the problem.
Service Learning and Community-Based Learning
Community-based learning (CBL) (also called service learning) integrate direct community engagement into academic courses to mutually benefit students and community partners. These approaches emphasize the development of students’ civic awareness, knowledge, skills, values and goals to produce tangible social change and promote students’ critical thinking, self-efficacy, interpersonal skills, civic and social responsibility, academic development, and educational success.
Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL)
POGIL is a structured protocol in which students work collaboratively to investigate a topic. This approach begins with the assumption that we learn and complete tasks more effectively in groups because everyone has gaps in their skillset and knowledge base. By pooling assets, students are more able to tackle complex problems, thereby facilitating higher order tasks and ultimately promoting better learning experiences. Key elements of the POGIL approach are the use of persistent teams who together work through challenging, inquiry-based problems and the assigning of roles within those teams that enable students to self-manage the group’s work. Faculty members serve as guides while students learn through the process of inquiry.
Team-based learning (TBL) engages student knowledge through individual testing and collaborative work in persistent teams. There are four essential elements of team-based learning: 1. Groups: Groups must be intentionally formed and managed. 2. Accountability: Students must be accountable for the quality of their individual and group work. 3. Feedback: Students must receive frequent and timely feedback. 4. Assignment design: Group assignments must promote both learning and team development. When these four elements are implemented in a course, the stage is set for student groups to evolve into cohesive learning teams.
The Flipped Classroom
In traditional classrooms, students consume content during class time, generally through listening to lectures. The flipped classroom moves more passive learning activities–such as listening, watching, or reading–outside of class time to make space within the classroom to practice skills and receive feedback. Students gain first exposure to content prior to class, ideally complete a knowledge check before coming to class so they and the professor can assess understanding ahead of the class period, and then participate in in-class or in-clinic activities that prompt higher-level thinking about the content through collaborative learning.
Gamification
We enjoy games because they’re fun, interactive and in many cases, capitalize on our competitive tendencies. There are many ways to bring the energy of play to the classroom by gamifying learning, ranging from easy-to-implement options such as using the “Competition” activity option in Poll Everywhere (for which Temple has an institutional license) to more complex activities such as Reacting to the Past (RTTP), a role-playing and immersive pedagogy. For example, our 2022 STEM Educators’ lecturer, Dr. André Thomas, described his successful creation of a video game designed to educate calculus students on the concept of limits. Where games are devised in such a way that they are enjoyable, involve collaboration, and require students to retrieve and apply course material, they are a surefire mechanism for encouraging engagement and information recall. And where they involve exploring and contextualizing a subject position that the student then must inhabit through an assigned role, as in RTTP, they allow for meaningful reflection on the complexities of contemporary and historical situations.
Executing long-term structured active learning
As mentioned above, long-term active learning techniques can require additional planning and intentional steps for ensuring group success. Faculty often ask us if there are ways to have students work more equitably and effectively in team projects. Asset-mapping can be used to promote equitable teamwork.
Asset Mapping
We know that student group projects can be a valuable experience for students. However, even with an equal distribution of work, they may not always be equitable. This can be especially true in disciplines where underrepresented and marginalized groups might be stereotyped as not being capable enough to handle the project. Consistent with prior research in STEM fields, Stoddard and Pfeifer from Worcester Polytechnic Institute’s required first-year interdisciplinary project-based learning course, women and students of color more frequently experienced their ideas being ignored or shut down, being assigned less important tasks, dealing with an overpowering teammate, and having their work go unacknowledged or claimed by others.
They employed an equity-based approach using asset mapping originally developed by Kretzman and McNight in 1993. In essence, asset mapping gives students the opportunity to get to know their and their team’s strengths, interests, identities, and needed areas of growth related to the project. But it goes well beyond that. Asset mapping is just the initial step of a process that enables students to take a deeper dive into bias and stereotyping as they evaluate their own behaviors and the dynamics of their teams. As a way to operationalize asset mapping, Stoddard and Pfeifer developed this toolkit containing three modules that include the tools, activities, assignments, and rubrics needed at different times of the semester.
If you’re interested in trying one of these longer-term active learning techniques, don’t hesitate to reach out to a CAT staff member for support. Stay tuned for the next installment of our active learning blog series which will focus on active learning in large classes!
___________________________________________________________________________
References
Amaral, G. (November 11, 2019). Using “Reacting to the Past” Role-Playing Games to Foster Vigorous Active Learning. EDvice Exchange Blog. Center for the Advancement of Teaching.
Association for Experiential Education. “What is Experiential Education?”
Bringle, R. G., & Clayton, P. H. (2012). Civic education through service learning: what, how, and why?. In Higher education and civic engagement: Comparative perspectives (pp. 101-124). New York: Palgrave Macmillan US.
Guo, P., Saab, N., Post, L. S., & Admiraal, W. (2020). A review of project-based learning in higher education: Student outcomes and measures. International journal of educational research, 102, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101586..
McLean, S. F. (2016). Case-Based Learning and its Application in Medical and Health-Care Fields: A Review of Worldwide Literature. Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 3. https://doi.org/10.4137/JMECD.S20377
Pereira, O. P., & Costa, C. A. (2019). Service Learning: Benefits of Another Learning Pedagogy. Economic Research, 3(9), 17-33.
Pfeifer, G., & Stoddard, E. A. (2018). Diversity, equity, and ınclusion tools for teamwork: asset mapping and team processing handbook.
Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning. Team-Based Learning.
Rouder, C. (March 21, 2022). A Game-based Approach to Teaching Calculus: Implications of the Research for STEM Courses. EDvice Exchange, Center for the Advancement of Teaching.
Team-Based Learning Collaborative. What is TBL: Overview.
The POGIL Project. General POGIL Book.
The POGIL Project. What is POGIL?
Thomson, B. (September 24, 2019) Flipping the Classroom. EDvice Exchange Blog. Center for the Advancement of Teaching.
Yew, E. H., & Goh, K. (2016). Problem-based learning: An overview of its process and impact on learning. Health professions education, 2(2), 75-79. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452301116300062
Another Look at Active Learning, Part 3: Peer & Collaborative Learning In The Classroom
Dana Dawson, Ph.D. and Jennifer Zaylea, MFA

In Another Look At Active Learning, part 2 of this series, we put forward several easy to implement active learning activities. Here we will focus on activities geared towards accomplishing depth of knowledge through peer and collaborative learning – encouraging a space for synthesizing rather than memorizing. Peer learning allows students to teach one another while expanding and solidifying their knowledge. Collaborative learning is similar to peer learning, but the students are grouped and work towards a common goal, all the while developing communication skills, learning from each other, and sharing their own unique perspectives.
Benefits of Peer and Collaborative Learning
One of the biggest benefits of using intentional peer and collaborative learning in the classroom is that it promotes a sense of belonging, self-efficacy and community among our students. Several decades of empirical research have demonstrated the positive relationship between effectively implemented collaborative learning and not only our students’ emotional health, but their achievement, effort, persistence, and motivation (Scager, 2016). Students get to know one another and to forge connections. Their discussions help challenge false beliefs that get in the way of learning, such as the belief that they are the only one who doesn’t understand a particular concept or is struggling with material. A student’s peer may find ways of explaining a concept that is more comprehensible than the explanations or examples we use. And the process of peer learning promotes the development of so-called “soft skills” such as empathetic listening, communication, collaboration and problem solving.
Teaching Students How to Do Group Work Successfully
Learning with and from peers requires skills that our students are often still developing. It may be necessary to teach students some of the skills required for successful peer learning such as assigning tasks, asking follow-up questions or expressing disagreement. Here are some suggestions and activities to develop peer learning skills:
- Talk explicitly with students about skills required for successful group work, particularly where they are tasked with completing a longer term project (more on that in the next blog). Discuss what active listening looks like in practice. Point out to students how you model these skills in your teaching. Stephen Brookfield’s “Conversational Moves” activity, described in Brookfield and Preskill’s Discussion As A Way Of Teaching: Tools and Techniques for Democratic Classrooms, can be a great way to introduce students to strategies for promoting effective discussion.
- Explore the role of emotion in peer learning. How do students feel when a teammate drops the ball? How does disagreement impact the experience of working in teams?
- Address specific approaches to managing disagreement and communicating when another student’s point is not clear. Discuss ground rules for discussion early in the semester and consider asking students to participate in the creation of guidelines. The Hopes and Fears Protocol can be a helpful tool for this process. You might also provide examples of language to use in order to disagree respectfully (“What I hear you say is… The way I think about this topic is…”).
- Help students develop skills pertinent to collaboration by assigning roles such as leader, recorder, reporter, devil’s advocate and/or time-keeper. Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning encourages the use of the role of Analyst or Reflector, which is an individual who considers and periodically reports to the group on how successfully the group is communicating and collaborating.
Considerations When Implementing Peer/Collaborative Learning Activities
- Articulate the “why” of the activity and how it relates to larger goals within the course and within students’ respective professions. For example, explain that a job in advertising is not an isolated work space; rather it is a highly collaborative work space where ideas and tasks are shared. Each person brings their own knowledge and skills, and participates in a reliable fashion. A manager will select group members as they deem appropriate, and it will often not be the grouping of friends that the students might be thinking. Remind students that developing collaboration skills in the classroom will hone their skills so that they can be more effective and successful professionals.
- Clear instructions are essential when it comes to active learning and it is especially important as individual activities build into peer/collaborative activities. Early on you might need to help students by breaking out the tasks associated with the activity so that they can determine the most useful path to follow in order to achieve the goal. Providing the students with the opportunity to write out a few of their task-related skills on an index card before groups are formed might help to ensure that students do not get stuck trying to figure out who can contribute what. Ensure students know whether the activity is part of their grade for a course, if that grade is individual or a group grade, and how the grade is determined.
- Make the deliverable something that is meaningful to the course and to the peer/collaborative groups. If the deliverable is considered “throw away” material, then the students are less likely to put much effort into the activity. Ensuring that the deliverable is something of value, like publishing their project on a public facing website, will encourage the students to actively participate as a whole rather than letting one or two students do all the work.
- Regular group check-in’s are a necessity in peer/collaborative work. However, feedback can also create negative division within the group dynamic. To keep the group dynamic healthy, there might be a regular meeting at the start of each class where the group members identify items on a checklist that have been, or need to be, completed and by whom. Then, at the end of each class, the task list is revisited to ensure that all tasks are listed. This might mean that group members are adding to the list as they find they need additional work in one area or another to achieve the goal. The task list keeps each member accountable for their contribution and acts as a reminder of that accountability. In addition to a group task list, encouraging students to offer one another constructive feedback during their sessions is a great way to further build healthy communication skills.
Activities that encourage peer and collaborative learning
Investigating AI
- Compare output – Students work in small groups using their own prompts to see how differently they might approach researching a topic.
- Work on prompts together – Students work in small groups to co-write prompts to get the best (most closely related) response to a question they know the answer to.
- Play “spot the AI generated content” – Faculty provide pre-generated content to student groups and ask the groups to vet the content.
- Prompt Engineering – Students compete to engineer prompts to generate a result you’ve tested and obtained beforehand.
- Prompting Competition – Have students compete in creating the best prompt to elicit the most complete, useful, or interesting output to a course-related question or topic. Formulating a useful prompt requires clear articulation of the student’s own understanding, and comparing results allows students to practice their analytical skills. (This one comes from our Survival Guide to AI and Teaching pt.4: Make AI Your Friend.)
Role play: Involve students in activities where they assume different roles and play out scenarios that you or they have created. Students might shy away from this activity if the focus is only on one group at a time, so you might consider having several groups role playing in front of one other group rather than the class.
Interpreted lecture: Ask individual students or small groups to provide a short summary of your professor’s lecture in varying increments (every 15-20 minutes). This works best if you inform students ahead of time that you will be calling on them for this purpose so that they will be prepared for the next study session. You may need to call on other students to fill in any gaps, or fill in the gaps yourself.
Case studies: Provide students with a case study or problem. Break students into groups of 3-5. Students work through the problem and present a proposed solution to the class. Note: students can be working on the same problem, or each team can receive a different problem.
Debates: Form teams of students. Each team takes a particular stance on an issue. Ask debaters to debate an issue based on evidence, to clearly state points, to logically organize their argument, and to be persuasive. Those not on a team are the judges.
Create a study guide: In pairs or groups, have students review their notes and create their own study guide. Review with the class as a whole.
Create possible board questions: In pairs or groups, have students draft questions that might appear on their board exams or other high stakes assessments.
Rotating Stations: Four to six white boards or poster-sized sticky notes are arranged around the room. Each has a different prompt at the top. Students circulate around the room, reading responses and adding their own.
Teach each other / Update your classmate: In groups, have students take turns trying to teach the rest of their group a section of material. This will help them (and you!) gauge the depth of their understanding on a particular topic/concept. You may also ask students to write a memo to a real or fictional student who missed the last class session. In the memo, they describe the missed content and anticipate why the information might be important for understanding new content.
Jigsaw:
Step 1: Organize students into a group of 4-6 people.
Step 2: Divide the day’s reading or lesson into 4-6 parts, and assign one student in each group to be responsible for a different segment.
Step 3: Give students time to learn and process their assigned segment independently.
Step 4: Put students who completed the same segment together into an “expert group” to talk about and process the details of their segment.
Step 5: Have students return to their original “Jigsaw” groups and take turns sharing the segments they’ve become experts on.
Snowball:
Step 1: Have students work in pairs for a few minutes to discuss a response to a prompt that you’ve given them.
Step 2: Direct each pair to sit with another pair and now share amongst the four of you.
Step 3: Repeat to form a group of 8.
Step 4: Repeat until you have your whole class as one group discussing the issue.
Formulate a report: Individually, students draft a report such as an incident report, a project report, meeting minutes, or progress reports, etc.. In small groups, peers review the report and suggest improvements. Individuals revise their reports and submit them. This activity is based on formulating Incident Reports, but the reports could be on a variety of subjects such as meetings, projects, medical reports, or other activities.
Peer review: In pairs or small groups have students peer review student-created materials such as documentation, treatment plans, exercise programs, or discharge recommendations. Students can meet as a group to discuss the findings. Once feedback is provided students revise the materials before submitting.
Operate a tool: In groups of 2 to 4, students practice operating a tool or piece of equipment. As each student takes a turn the rest of the group provides them with feedback on their use of the tool.
Pass the Answer: Students write the answer to a prompt on an index card. They then swap answers with a nearby colleague. Turn and repeat swapping with someone else. Then swap one more time with someone else nearby. The instructor then calls on students to read the answer they are holding. This makes it easier for students to speak out in a large lecture hall, because they are offering someone else’s answer rather than their own.
As we mentioned in blog post 2 of this series, you do not need to implement all of the activities listed above. We encourage you to use an activity or two during your class sessions and to select activities that are designed to meet the learning goals of your course. Once the activities are completed, reflect and determine if those activities helped to accomplish peer and collaborative learning. Peer and collaborative learning are learned skills just like any course content you might be delivering. Students have a similar learning curve when it comes to communication. Build in the time for this learning when you are creating peer/collaborative learning activities.
References:
Scager, Karin et al. “Collaborative Learning in Higher Education: Evoking Positive Interdependence.” CBE life sciences education vol. 15,4 (2016): ar69. doi:10.1187/cbe.16-07-0219
Brookfield, Stephen D. and Stephen Preskill. Discussion As A Way Of Teaching: Tools and Techniques for Democratic Classrooms. 2nd Edition. Jossey Bass, 2005
Another Look at Active Learning, Part 2: The World’s Easiest Learning Activities
Jennifer Zaylea and Jeff Rients

Hearing fellow faculty talk about their activities in class might beg the question, “How do you deliver all of your content if you are “playing” during class time?” Yet, if you really think deeply about it, isn’t the application of the content the real goal? Ensuring that the students are able to conceptualize and apply the information in meaningful ways is what we strive for as faculty. As mentioned in the introduction to this series, a meta-analysis of 225 studies, put forth by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), revealed that STEM courses taught using active learning methods showed an increase of approximately 6% higher exam scores than non-active lecture courses and that the failure rate was 1.5% higher in traditional lecture courses (p. 8410).
A common concern we hear is that active learning techniques take up class time that should be spent on covering the vast list of required content for the course. Rather than being overly concerned with covering content in class, we can provide students the opportunity to cover at least some of the content outside of class. This allows for time to implement and practice the concepts during in-class activities where students can receive immediate feedback from their peers and faculty.
Using active learning techniques in-class does not mean that you are less needed. In fact, if you have designed your activities to help build the students’ self confidence in the material, then you’re actually very busy with facilitation of the activity and feedback or guidance. The learning is happening in real-time rather than a few hours, days, weeks after an assignment has been submitted. This approach affords you the opportunity to see where students might need additional support or where they have mastered certain content.
Below are a few basic active learning activities that are easy to implement in the classroom as you begin your exploration of new methods that can support an engaging learning environment.
- The Strategic Pause – Following 10 or 15 minutes of lecturing, announce something like “Before moving on, I am going to pause for a minute to allow you to catch up with your notes and decide if you have any questions.” This allows time for reflection, assimilation and retention of class material. Note that the first time you use this simple technique a full sixty seconds will feel like forever.
- Think-Pair-Share – One of the simplest but most effective ways to improve classroom discussions, a Think-Pair-Share begins with the instructor posing a question. Students individually contemplate this question for a minute or two (the Think step), then share their thoughts on the topic with the person sitting next to them (the Pair step), and conclude with a whole group discussion (the Share). This method gives students time to think their own thoughts and test them out in private, leaving them better prepared to participate in a class-wide discussion.
- Polling – Polling can be used in a variety of ways, such as asking your students to quickly offer a new idea on a topic, and the responses can be seen in real-time by the class. A single question poll following the presentation of a difficult topic can allow you to see if the students are ready to move on or if they need additional instruction on the current topic. Polling can be done with a simple show of hands, but more anonymous options, such as using polleverywhere.com or colored index cards, ensures more accurate results.
- Gamification/Challenges – Temporarily turning your classroom into a Jeopardy game or an online scavenger hunt provides an opportunity for students to engage in friendly competition while flexing their learning and building social connections.
- Concept Mapping – Students, using their own words and diagrams, make a visual that maps out the connections between course content. Concept mapping activates learning and retention of knowledge by requiring students to organize content in their own unique way. A concept map can be used as an additive organizational structure to build upon prior knowledge, brainstorming, conceptualizing connections. Asking students to compare concept maps or collaborate on creating one often reveals gaps in learning. Concept maps can be hand-drawn, produced with various graphic applications, or built with online whiteboard tools such as padlet.com or miro.com.
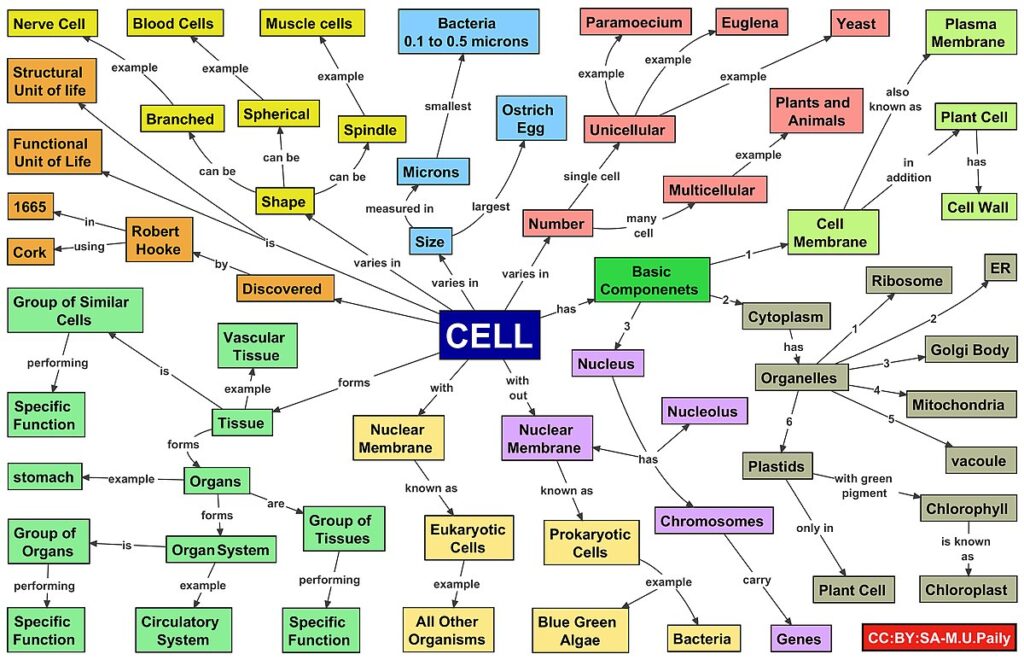
An example of an elaborate concept map.
- One-Minute Paper – A quick written task asking the students to summarize what they learned during the class and/or what they do not understand. One-minute papers can be completed on index cards and are usually low or no stakes. Consider asking students not to put their name on their One-Minute Paper, as you will get more honest and revealing answers to prompts focusing on where the students are still struggling.
A Helpful Hint
Don’t immediately try to implement every activity in every class. You will become frustrated and so will your students. Use the activities as they relate to and enhance your content and its implementation. Some activities will be less successful than others in your particular learning context, and this is part of learning what works for your students and your course objectives. But also keep in mind that facilitating learning activities is a skill and, like any skill, practice leads to improvement.
Temple Faculty who would like assistance planning a learning activity for their students, please remember that the CAT is here to help! Make an appointment to speak with one of our pedagogy specialists.
References
Freeman, S., Eddy, S.L., McDonough, M., Smith, M.K., Okorafor, N., Jordt, H., and Wenderoth, M.P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), 111(23), 8410-8415.
Jennifer Zaylea is Digital Media Specialist at Temple’s Center for the Advancement of Teaching (CAT). Jeff Rients is Associate Director of Teaching and Learning Innovation at the CAT.

Cell Concept Map image by M.U.Paily made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
Another Look at Active Learning: A Blog Series, Part I
Stephanie Laggini Fiore

If I had a quarter for every time someone says something to me like “I had 4 years of French in high school and I don’t remember a word of it”, I could pay for a trip to Hawaii right now. As a world language instructor, I hate hearing that. I want everyone who studies language to feel as if they can travel and be able to communicate in the target language in everyday situations. But, of course, the way language was taught when I was younger was not effective in making this ultimate goal a reality. Plug-and-chug homework exercises, rote drills, and mandates to memorize long lists of vocabulary and verb tenses were the dominant modes of teaching. As anyone who has memorized loads of content for an exam and then promptly forgotten it can attest to, mastery and retention of information and the ability to apply it in varied situations is not served well by these methods.
What we know from decades of research on learning is that students learn best through active learning. (If you love lectures, don’t stop reading!! I’ll get to you in a minute.) Active learning engages students in the work of learning. It asks them to do more than just absorb information by listening to the experts tell them what to think. Instead, they participate in a wide variety of activities that ask them to cognitively engage with the course content by assessing their own knowledge of a topic, collaborating with others to solve problems, discussing key points, analyzing and evaluating information, and more. In active learning environments, students are moved beyond the remembering level of Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain to higher order levels of thinking that lead to deep learning.
In 2014, Scott Freeman et al. published a meta-analysis of 225 studies on active learning (Freeman et al., 2014), in which they found that average grades on exams in active learning classes increased by half a letter grade, and that failure rates were 55% lower in active learning classes rather than in classes that utilized traditional lecturing (Again, hold on lecturers. I’m getting to you!) Freeman’s comment in an interview in Wired is telling: “The impact of these data should be like the Surgeon General’s report on ‘Smoking and Health’ in 1964–they should put to rest any debate about whether active learning is more effective than lecturing” (Wired, May 12, 2014). Since that time, research continues to add evidence to point us to the benefits of “hands-on” and “minds-on” learning (Yannier et al., 2021) and the increased benefits of active learning environments for underrepresented students (Eddy & Hogan, 2017), while a recent literature review adds that active learning environments also benefit students’ well-being (Ribeiro-Silva et al., 2022).
But what about lectures, you say? (See, I told you I’d get to you!) Students aren’t experts, so they would learn better from an expert, right? There is a place for lectures done well. The false dichotomy that embracing active learning means throwing lectures out entirely is unhelpful. As Stephen Brookfield reminds us, lectures are useful for explaining complex concepts with clarifying examples, introducing alternative perspectives, and modeling intellectual attitudes and behaviors. But a traditional lecture—that is, all-lecture-all-the- time—showcases what you know as the expert, but does not work well to bring novice learners along for the intellectual ride. When the dominant voice you hear in the room is your own, it’s time to stop and take stock of the teaching methods you are using. The best lecturers pause to ask questions, use demonstrations and media to support the point they are making, give students time for reflection—in short, they use active learning techniques embedded in their lectures to help students learn.
Today, in world language classes, students begin using the language from day one. They still need to memorize information, but it is in service to the actual use of the language. They make plenty of mistakes, but I remind them that struggle is part of learning and that they will come to a point where they are feeling less struggle and more triumph in their learning journey. It’s also scary. Instead of reading from pre-written scripts, they are creating language on the spot without a safety net. That mirrors authentic use of the language and helps them navigate real situations when they are faced with them. A supportive atmosphere that encourages experimentation and active effort in using the language, de-emphasizes perfection, and supports resilience in learning is what it’s all about. The best part is that we all enjoy learning so much more.
You and your students can too! There is a continuum of active learning strategies available to instructors, starting from simple and informal think-pair-share activities and brief polling questions that take a few minutes, all the way to semester-long and highly structured team-based learning activities that require intentional preparation. You can dip your toe in, starting out small with just a few strategies, or dive into active learning wholeheartedly. In this blog series, we will guide you through your choices, explore how to employ active learning in online and large class environments, and also consider how to set up active learning for success. We hope you’ll join us and try some active learning strategies on for size.
Stephanie Fiore, PhD, is Associate Vice Provost and Senior Director of Temple’s Center for the Advancement of Teaching.
Grouping by Strengths
by Meg Steinweg and Melanie Trexler

Faculty frequently design team projects to enable students to accomplish tasks they cannot complete alone and to build teamwork skills. The latter, according to the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE), is one of the top eight career-readiness skills that students need to learn in college (NACE 2022). Yet, instructors face a common challenge: How do you put students in groups that work well together?
The following activity helps instructors create groups that incorporate students self-determined strengths, student choice, and instructor matching-making. Additionally, the assignment invites students to reflect on their strengths and express agency in choosing their group members.
Part I: Strengths Assessment
- Access https://high5test.com/ – Select “Find Your Top Strengths”
- Take the 100 question High5 Test. (8–15 minutes) Answer as best you can.
- Read and reflect on your results.
Part 2: Write the Paper
Reflect critically on the five strengths as they relate to your life and to your role in a group. For each of the five strengths:
- State the strength
- Describe it. Copy and paste the paragraph about your strength from the High5 website.
- Write a paragraph noting where you see this strength appear in your own life and in how you work in groups. Use examples of group work in other classes, on teams (ex: sports, volunteering, etc.), and/or in internships or jobs.
- Conclusion: Do you think these describe your core strengths as an individual? Why?
Part 3: Presentation
Present your strengths to the class in a 2–3-minute presentation.* Highlight at least 2 strengths you possess. How do you use these strengths in a group? Why are you a valuable team member? What are strengths you are looking for in a group member? Why?
*This could be recorded, and presentations viewed by students outside of class.
Part 4: Listening and group member selection write-up
As you listen to your peer’s presentations consider how peers’ skills and strengths compliment your own. You do have a voice in choosing potential group members, though the instructor determines which groups work together. You will be in a team with at least one person you select.
- In order, list four group members you would like to work with.
- In one paragraph per person (3–4 sentences), explain:
- How do your strengths complement each other in a group project?
- What is one possible way your strengths could clash and how could you overcome that challenge?
- How do your strengths complement each other in a group project?
Meg Steinweg is Associate Professor of Biology at Roanoke College. Melanie Trexler is Associate Professor of Religion at Roanoke.
This article was released under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) license as part of the Teaching Messages Collection 2023-24.


