MERLOT is a well-known repository of openly accessible learning content produced and shared by higher education faculty. With its thousands of learning objects, MERLOT is considered a reliable source of quality Open Educational Resources (OER).
Faculty are sometimes challenged to find OER that fits their course. To enhance their ability to locate OER, MERLOT has developed a new feature called “Smart Search”. It extends access to online learning materials well beyond MERLOT’s curated and peer reviewed collection. Smart Search helps to answer the pervasive and nagging question, “Where can I find OERs?”
Smart Search searches the World Wide Web specifically for the kinds of learning materials typically found in MERLOT. It uses a proprietary MERLOT user profile design to find the newest and most popular learning materials on the web. While these web items are not reviewed or curated as is the MERLOT resources, searches can recommend materials they find for future review.
Smart Search is easy to use. From the MERLOT home page go to the search feature:
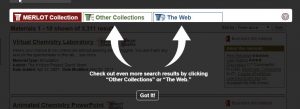
Then MERLOT will indicate you have a choice of three options for finding content:
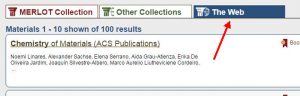
Choosing the Web search option will result in up to 100 websites with potential OER content on the search topic:
As part of Temple University Libraries celebration of Open Education Week, we encourage all instructors to visit MERLOT and consider ways in which OER could be used to offer students affordable learning material. For more information on locating OER resources, using existing library content or other resources as affordable learning materials contact Steven Bell, Associate University Librarian.