In late July, Netflix released a much anticipated prequel to the quite literally campy cult classic Wet Hot American Summer which premiered in the U.S. in 2001. The newly released series and the original movie both revolve around the often deviant misadventures of camp goers at a disorganized sleep-away camp in Maine called Camp Firewood. Both films are loosely based on the experiences their director, David Wain, had while attending a Jewish camp in Belgrade, Maine.
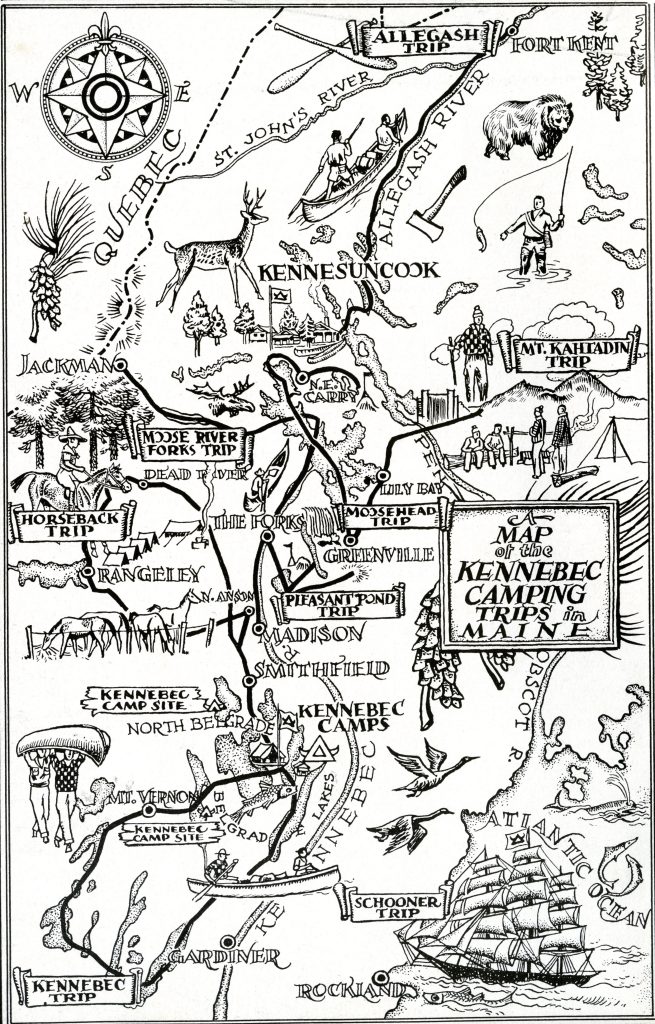
Established by three Jewish Philadelphians, Louis Fleischer, Charles Edwin Fox, and Milton Katzenberg, at the start of the twentieth century, Camp Kennebec was located in the scenic Kennebec County town, Belgrade. For almost a century, it catered to Jewish male youth ages 8 to 18, mainly hailing from Philly.
Camp Kennebec’s location and religious affiliation are likely the only similarities between it and David Wain’s camp memories. Kennebec was a no-nonsense kind of summer experience with few amenities. It was established to mold boys into “true men” during the tail end of the Progressive Era, when stoic masculinity was emphasized.
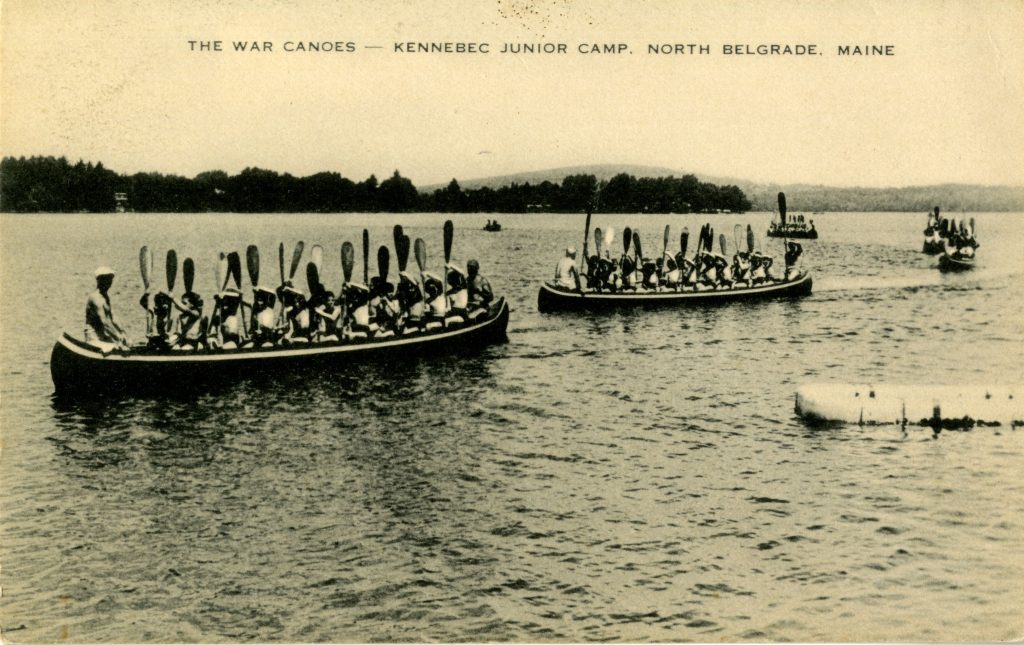
Camp Kennebec recruited counselors from Princeton, Harvard, Yale, and the University of Pennsylvania among other universities, and instructed campers to call each of them “uncle” (or the “uncs” as one camper affectionately noted in his photographic travel journal). Kennebec’s primary emphasis was on the development of respectable traits such as masculinity, ruggedness, and independence. Kennebec’s campers engaged in athleticism, wilderness survival, and first aid, but also academic pursuits such as the study of literature. For many, the boyhood bonds formed at the camp and the lessons it taught them lasted well into adulthood.
A collection of records from Camp Kennebec and Kennebec alumni is available for research in Temple University Libraries’ Special Collections Research Center. The collection includes yearbooks, souvenirs, photo albums of hiking trips, and ephemera relating to alumni reunions, which were no doubt well attended. To learn more about Camp Kennebec and the alumni collection, view the online finding aid.
-Irena Frumkin, SCRC Student Assistant