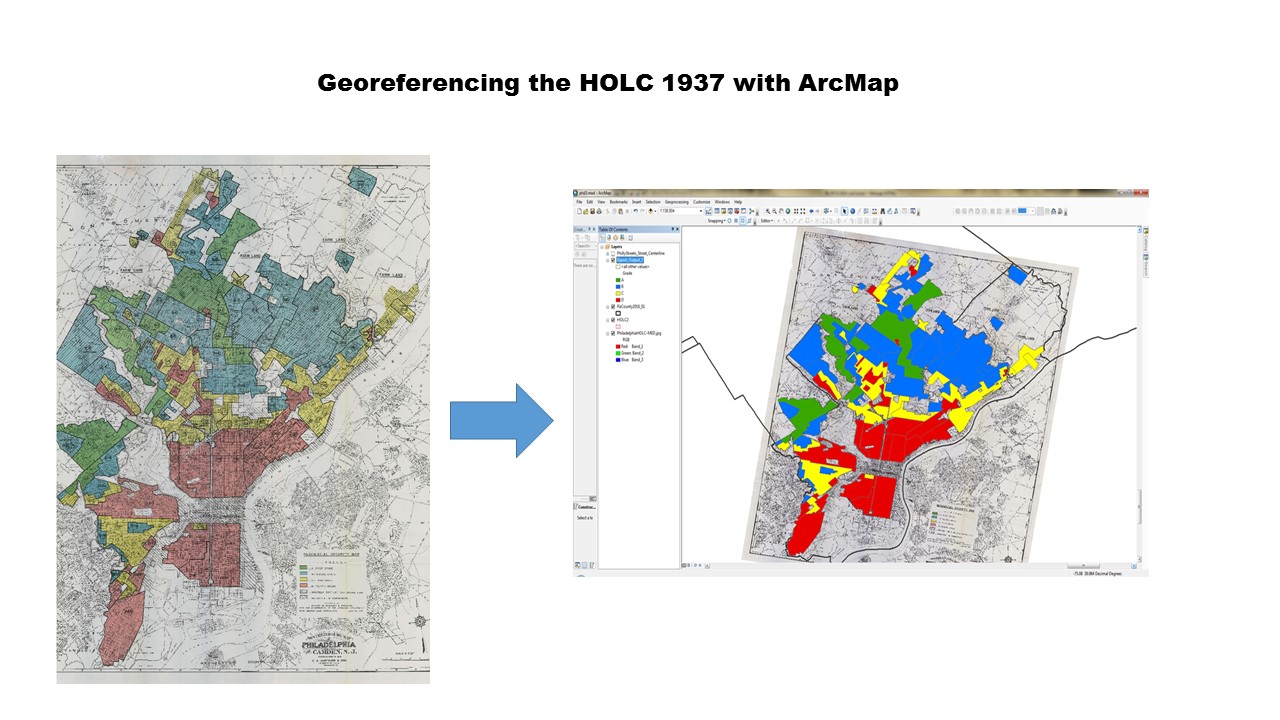
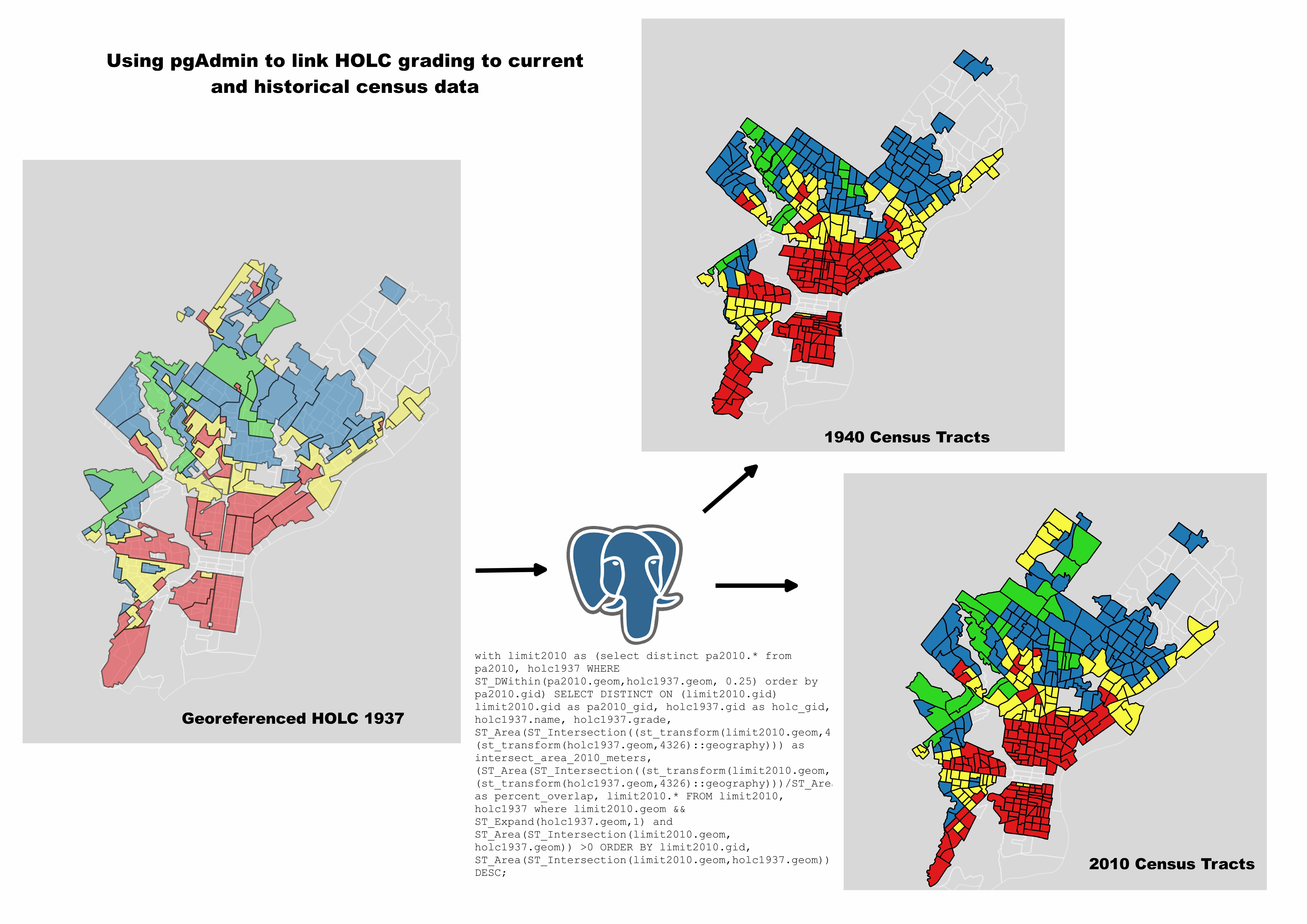
For my capstone project, I will be working with Pennsylvania Horticulture Society to develop a streamlined data management system for their LandCare Program. The LandCare Program strives to rehabilitate vacant land parcels in the city of Philadelphia to address urban revitalization and land vacancy issues plaguing the city. The image below shows what some of these land areas can look like.

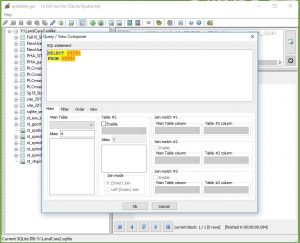
The project has so far consisted of the construction of a database in SpatiaLite to work with the shapefiles for the project, see the image below for an overview of the GUI. I selected SpatiaLite as it uses the SQLite language and connects seamlessly with ArcMap. This ultimately allows the user to create an manipulate geodatabases using code written in SpatiaLite and immediately access the results in ArcMap.
My first sprint (May 30th to June 8th) consisted primarily in the set up of documentation for the project, in addition to the following items: creating a geodatabase, working to remove sites that have new uses (no longer PHS LandCare sites) as well as writing base code for updating tables based on an excel.
The process to create documentation was decided upon so formal directions would be available for anyone working on this project in the future. In addition to this, I have detailed notes of what I have done thus far and can change information as the project progresses.
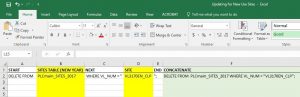
Most of the coding that has been done thus far has been metacoded in excel. By doing this, the overall update process is now streamlined to where someone with no SQL experience can use the excel and get valid results. Using the image below, an example to delete a row from a table in SpatiaLite, it is visible that the user only must input a small amount of information such as the table name and the identifier for the row being deleted. This will benefit not only the inexperienced coder in the future, but also anyone who must update many files at once as only one column must be manipulated. The end result will be to gain statements that can be copied and pasted in the query window of SpatiaLite.
So far, there are metacoding files for updating new use sites and updating columns overall. When updating new use sites, we must copy information from both parcels (individual lots) and sites (many lots together) to develop one overarching row of data. This process was broken down into four steps, two with updates and two for deleting the land area from the new parcel and site tables as they are no longer in the maintenance database. The individual update metacoding was created for a quick update like square feet. Using this process, much information can be quickly added to the pre-written code and then executed in SpatiaLite.
Finally, in sprint two, the next process will be determining the process to update parcel and site data for address changes. As many sites may lose a parcel or gain a parcel over the course of the year for maintenance purposes, it is important that adequate files are maintained on current geometries. This will most likely be completed again with many steps in the form of a metacoded file.