Big Data
Recommendation
- Article
- China
- Econometrics, Big Data
Yang, Lisi; Yang, Yang; Huang, Xijia; Yan, Kai
- Article
- US
- Econometrics, Big Data
Zhang, Xiaowei; Huang, Xingyu; Yang, Yang; Liu, Wei
- Article
- US
- Econometrics, Big Data
Zhang, Ziqiong; Yang, Yang; Wang, Xueyan; Wang, Chuxin; Zhang, Zili
Related Presentations
- Presentation
- 01/02/2025
Spatial Analytics
Workshop on Informatics, Data Science, and Economics in Hospitality and Tourism Research
University of Houston, Houston, TX
- Invited Talk
- 03/04/2024
COVID19tourism Index and its application in tourism management
University of Perpignan
Perpignan, France
- Invited Talk
- 03/08/2023
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Research in Tourism and Hospitality
University of Macau
Macau (Online)
- Invited Talk
- 09/17/2021
Tourist behavior analysis using online user generated data
Kyung Hee University
Seoul, Korea (Online)
Related Resources
- Tool
PS-SAT: Predictive Scheduling & Satisfaction Analytics Tool
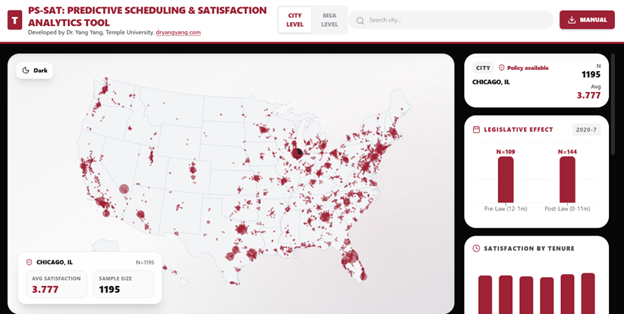
This web-based dashboard is designed to visualize tourism and hospitality employee satisfaction data across U.S. geographic units at both the City and Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) levels. The application provides interactive mapping, subgroup breakdowns, and (where applicable) legislative pre– and post–comparisons.
Key Features:
- Dual-Level Geographic View: Users can switch between City-Level (point markers) and MSA-Level (polygon map) visualization.
- Interactive Search & Selection: Users can search locations dynamically and select them either via the map or the dropdown search interface.
- Subgroup Breakdown Analysis: Satisfaction scores are displayed by:
-
- Job tenure
- Business model
- Skill level
- Front-of-house vs. back-of-house
- Legislative Effect Comparison: For locations with valid policy-period data, the dashboard displays Pre-Law vs. Post-Law satisfaction comparisons.
- Visual Encoding of Sample Size: City marker size scales with sample size (N), allowing immediate identification of data-rich locations.
- Dataset
Government Attention to Tourism Data
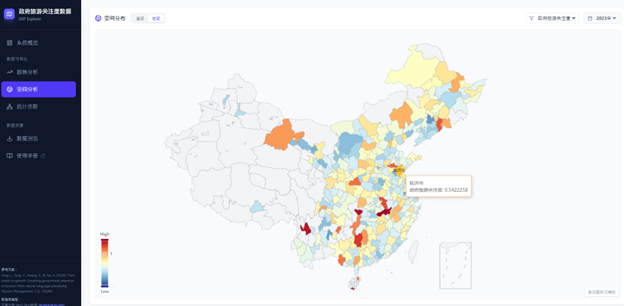
This web-based application is designed to provide researchers and policymakers with an interactive platform for querying and analyzing data regarding Government Attention to Tourism (GAT) in China.
Based on the research findings of Yang, Yang, Huang & Yan (2026), this tool visually demonstrates the spatiotemporal relationships and statistical correlations between the GAT index and various tourism economic indicators. This tool supports a bilingual interface in both Chinese and English. You can switch between the two language modes in real-time by clicking the language toggle button (中文/EN) located in the top-right corner of the page.
Key Features:
Multidimensional Data Coverage: Includes GAT indices and 11 key tourism economic indicators at both the provincial and prefectural (city) levels.
Interactive Visualization: Provides trend analysis, spatial distribution maps, and statistical correlation scatter plots.
Data Resources: Supports viewing summaries of raw data and downloading data.
Tool Link: https://uflyy.github.io/gat-database/
本网页应用旨在为研究人员和政策制定者提供关于中国政府旅游关注度 (Government Attention to Tourism, GAT) 的交互式数据查询与分析平台。
该工具基于 Yang, Yang, Huang & Yan (2026) 的研究成果,通过可视化手段展示了 GAT 指数与各类旅游经济指标之间的时空关系和统计关联。本工具支持中英文双语界面。点击页面右上角的语言切换按钮(中文/EN),即可在两种语言模式间实时切换。
核心功能:
- 多维数据覆盖: 包含省级和地级层面的 GAT 指数及 11 项关键旅游经济指标。
- 交互式可视化: 提供趋势分析、空间分布地图和统计关联散点图。
- 数据资源: 支持查看原始数据摘要及下载。
- Dataset
Pulse of American Domestic Tourism
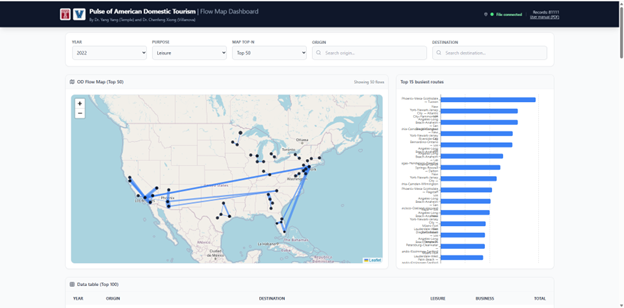
“The ‘Pulse of American Domestic Tourism’ project serves as a digital monitor for the nation’s internal mobility. By mining transportation-derived mobility data, we develop a comprehensive matrix of tourism flows connecting American MSAs. This data-driven approach unveils the rhythmic shifts in visitor demand and regional connectivity. Crucially, we ground these digital insights through extensive cross-validation with household survey data, creating a verified, high-resolution framework for understanding the evolving landscape of domestic travel.”
Key Vocabulary Used (Why it works):
- Inter-MSA travel flows: Specific and accurate to your methodology.
- Arterial circulation / Rhythmic shifts: Reinforces the “Pulse” metaphor without being cheesy.
- High-granularity / Spatiotemporal precision: Highlights the “Big Data” advantage.
- Rigorously cross-validated: Emphasizes the reliability of your model (crucial for academic trust).
- Ground-truth metrics: A professional way to refer to the survey data as the standard of truth.

You must be logged in to post a comment.