JOURNAL OF TRAVEL RESEARCH
A spatial econometric approach to model spillover effects in tourism flows
- 2012
- JOURNAL OF TRAVEL RESEARCH
- 10.1177/0047287512437855
Yang, Yang; Wong, Kevin K. F.
Abstract
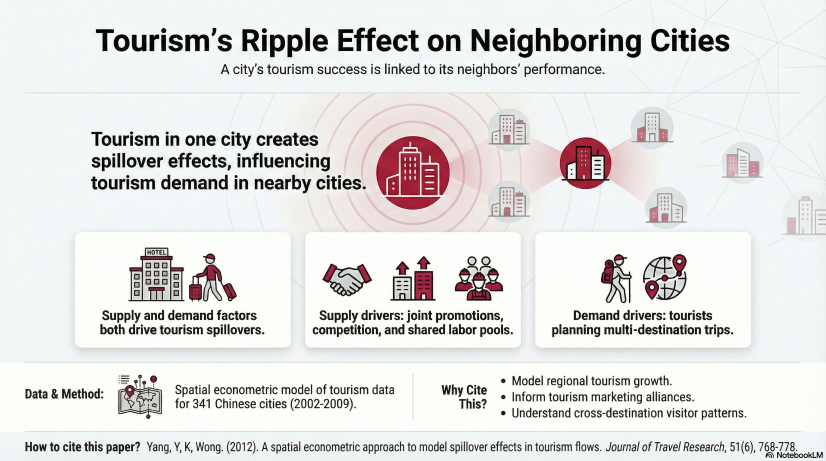
The main purpose of this research is to investigate and estimate the spillover effects in inbound and domestic tourism flows to 341 cities in mainland China. In conjunction with this, the key determinants of tourism flows are also studied in the spatial econometric model. The results confirm the existence of spillover effects in both inbound and domestic tourism flows, and suggest that physical infrastructure factors, tourist attractions, and the SARS outbreak are significant determinants of inbound and domestic tourism flows. In addition, it is found that although the degree of openness to inbound tourists is important for inbound tourism flows, a city’s income is the key to enhancing domestic tourism flows. Significant differences in spillover effects and determinants of tourism flows are also discovered between cities in different regions.
Keywords
spillover effects; tourism flows; spatial econometric model; China
Research topic
Tourist Flows and Location
Research method
Econometrics, Spatial Modeling
Geographic area
China
AI Audio Overview
AI Infographic