Introduction:
-An important factor in stroke rehabilitation includes repetition of specific movements to improve functional mobility and balance.
-Wii technology provides an alternative form of repetitive task training in an interactive enriched environment for patients to improve functional mobility and balance.

Clinical Case & PICO:
-55 y.o. male Starbucks Manager who suffered from cerebral vascular accident in the right middle cerebral artery
- Ambulates 10’ with hemi-walker with max assist for balance at a self-selected speed of 0.2 m/s,
- Unable to perform TUG at this time due to inability to maintain standing balance without assistance
- Scored 3/56 on Berg Balance Test
- Goal is to return to work and participate in outdoor activities with family.
PICO:
Is using Nintendo Wii an effective intervention for stroke patients to improve balance compared to the conventional physical therapy (CPT)?

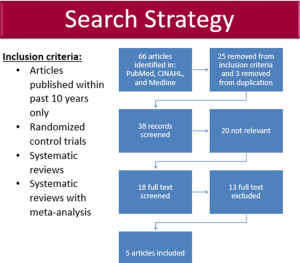
Search Strategy:
Inclusion criteria:
- Articles published within past 10 years only
- Randomized control trials
- Systematic reviews
- Systematic reviews with meta-analysis
- 66 articles identified in: PubMed, CINAHL, and Medline
- 25 removed from inclusion criteria and 3 removed from duplication
- 38 records screened
- 20 not relevant
- 18 full text screened
- 13 full text excluded
- 5 articles included
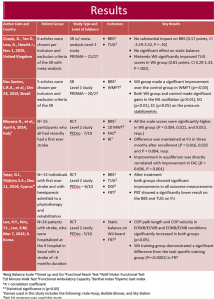
Results:
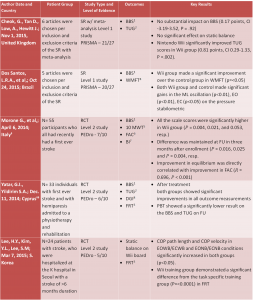
1-Berg Balance Scale 2-Timed up and Go 3-Functinal Reach Test 4-Wolf Motor Functional Test
5-10 Meter Walk Test 6-Functional Ambulatory Capacity 7-Barthel Index 8-Dyamic Gait Index
*R = correlation coefficient
**Statistical significance is (p<0.05)
ꭞGames used in this study includes the following: Hula Hoop, Bubble Blower, and Sky Slalom
ꭞꭞWii Fit program was used this study
ꭞꭞꭞGames used in this study includes the following: Tightrope Walking, Penguin Teeter-Tooter Seesaw, Balance Skiing, Rolling Marble Board, and Balance Wii
Clinical Bottom Line:
-The use of Nintendo Wii is an effective way to improve static and dynamic balance in post-stroke patients however, there is no significant difference between the Nintendo Wii and conventional physical therapy.
-Both level 1 and level 2 studies state that combining the Nintendo Wii and conventional physical therapy will produce the best results.

Application to Case:
-Since the Wii is just as effective as CPT, it would be an appropriate intervention to incorporate into the patient’s plan of care.
-Pt will participate in 45-60 minutes of CPT which will include static and dynamic balance training using stable ground, foam boards, and interventions from the berg balance scale, gait training using LRD, and specific tasks oriented to training ADLs for 5x/week in addition to 30-45 min of Wii for 3x/week for 6 weeks. Games will include ski slalom, ski jump, Wii sports, soccer heading, hula hoop, and penguin slide game.
-Physical therapist will give less assistance as patient improves in balance and increase the difficulty in Wii games.

Limitations:
-Has a small sample size for all randomized control trials
-Balance data was acquired using less sensitive outcome measurements instead of a stabilometry which would give the best quantitative data
-Lack of long-term follow-up

References:
- Cheok G, Tan D, Low A, Hewitt J. Is nintendo wii an effective intervention for individuals with stroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(11):923-932. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2015.06.010 [doi].
- Dos Santos LR, Carregosa AA, Masruha MR, et al. The use of nintendo wii in the rehabilitation of poststroke patients: A systematic review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;24(10):2298-2305. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.06.010 [doi].
- Lee HY, Kim YL, Lee SM. Effects of virtual reality-based training and task-oriented training on balance performance in stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(6):1883-1888. http://libproxy.temple.edu/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com.libproxy.temple.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm&AN=26180341&site=ehost-live&scope=site. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1883.
- Morone G, Tramontano M, Iosa M, et al. The efficacy of balance training with video game-based therapy in subacute stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:580861. doi: 10.1155/2014/580861 [doi].
- Yatar GI, Yildirim SA. Wii fit balance training or progressive balance training in patients with chronic stroke: A randomised controlled trial. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(4):1145-1151. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1145 [doi].