Network analysis can be an extremely beneficial tool for any organization which relies on GIS to understand the area it serves. This is particularly true if the organization deals primarily with transportation or the distribution of goods. The network analysis package through ArcGIS allows organizations to gain critical insight into how people and goods move around within their designated service or study area. More specifically, the engineers that I work with at McMahon utilize GIS network analysis to gain enhanced insight on the regions in which they serve as transportation engineers and planners. The baseline method of analysis utilized is creating a service area layer, or series of layers, to gain an understanding of how much distance can be traveled on a road network given a set of parameters.
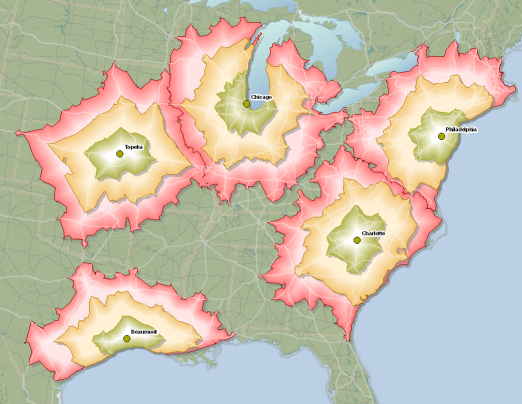
A Basic Example of a Service Area Layer, With Three Interval Breaks
The first step in creating a service area layer is to create a network dataset. A network dataset is a special type of ESRI dataset, which contains both spatial layers and network layers, as well as custom preferences and parameters to fine tune the output of the network dataset. To create a network dataset, first, download a road network layer that represents the area in which you want to create service areas. Often times, these layers are available from government agencies. For example, all Pennsylvania state and local roads are available on PASDA, provided by PennDOT. Once the streets / roads layer is downloaded, it is important to clip the layer to what you expect you might utilize from the service area analysis. If you choose not to clip the layer, you may find creating and working with the network dataset to be slow and difficult to manage.
You will also need to create a source point file that will represent the location or locations from which the service areas will be generated. You can create the actual points either now or after the network dataset is created, but the point feature class itself needs to be created beforehand. You will also need to create a file geodatabase and feature dataset to store all of these layers and datasets in.
Once the layer is downloaded, clipped, and present in your working directory with the source point file you can create the network dataset. This can be done by right-clicking inside any feature dataset and clicking new > network dataset. A dialog window should appear with options regarding the new network dataset. Name the network dataset and click next. You can leave most of the settings at their default values unless otherwise instructed or if you know the network dataset will be used for purposes in addition to creating a service area. Finally, on the second to last page of options, check the box next to “build service area indexes”. This will speed up the creation of service areas in the future.
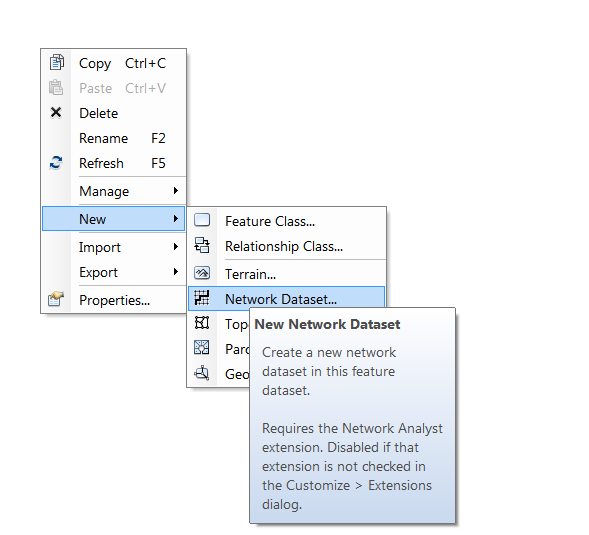
Creating a New Network Dataset Inside of a Feature Dataset
Click finish, and you will be asked if you want to build the network dataset. Click Yes. Once the network dataset has been created, open ArcMap and bring the newly created network dataset into the dataframe. When prompted to bring in any associated layers, say yes. Add the Network Analyst toolbar and click “New Service Area” under the Network Analyst dropdown.
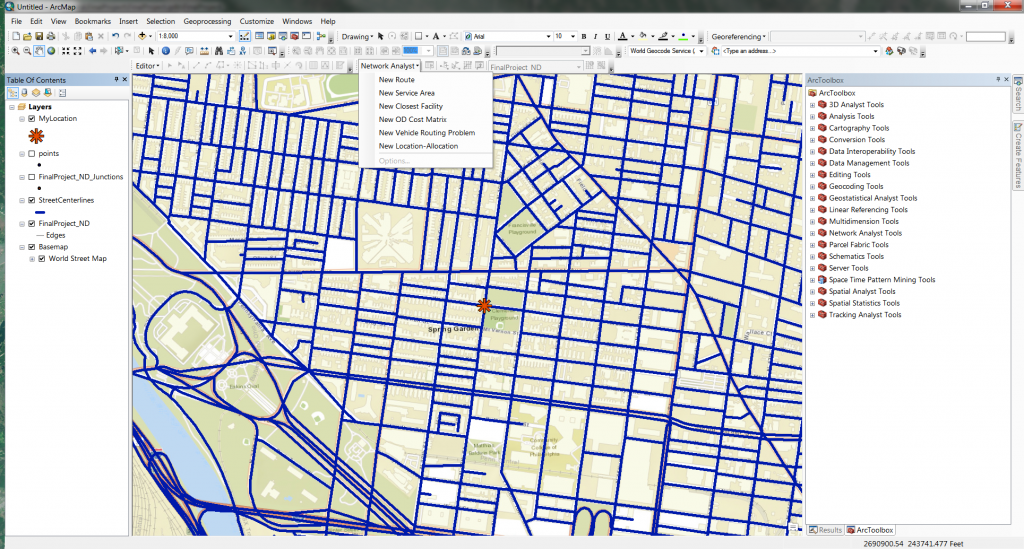
Creating a New Service Area with Network Analyst
Click the button directly to the right of the Network Analyst dropdown, to open Network Analyst Window. Here, you can load any origin points (previously created), polygon or line barriers, as well as set options for the service area that is going to be created. You can drag the point layer which contains the origin points into the Facilities group. Clicking the Service Area Properties button (top right corner of the Network Analyst Window) will allow you to set important preferences for the service area that is about to be created. Some of the most useful settings include the accumulation tab, which allows you to track distance and time along the service area, and the analysis settings tab. The analysis settings tab will allow you to set the direction of the service area, as well as any breaks, and to implement a temporal aspect to the service area.
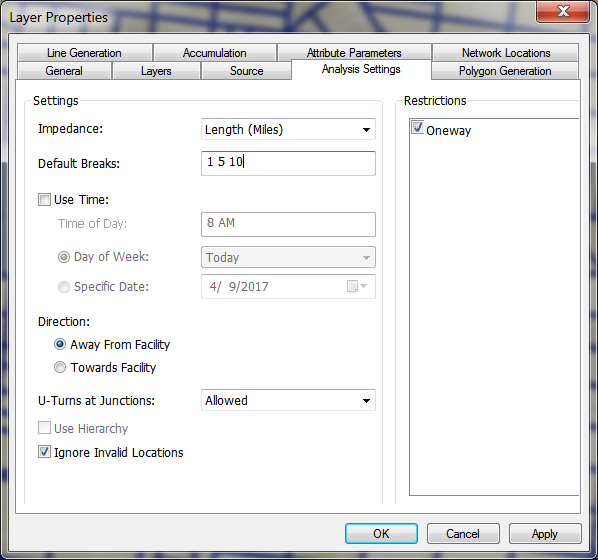
Service Area Properties
Apply any preferences and settings that have changed, and close the service area properties window. When everything is configured as desired, click the Solve button on the network analyst toolbar to run the analysis and create the service area. The analysis can be re-run an infinite number of times, and with the service area index that was created earlier, creating a service area should not take long each time. This way, you can tweak and fine tune the service area quickly and easily until you gain the desired result.
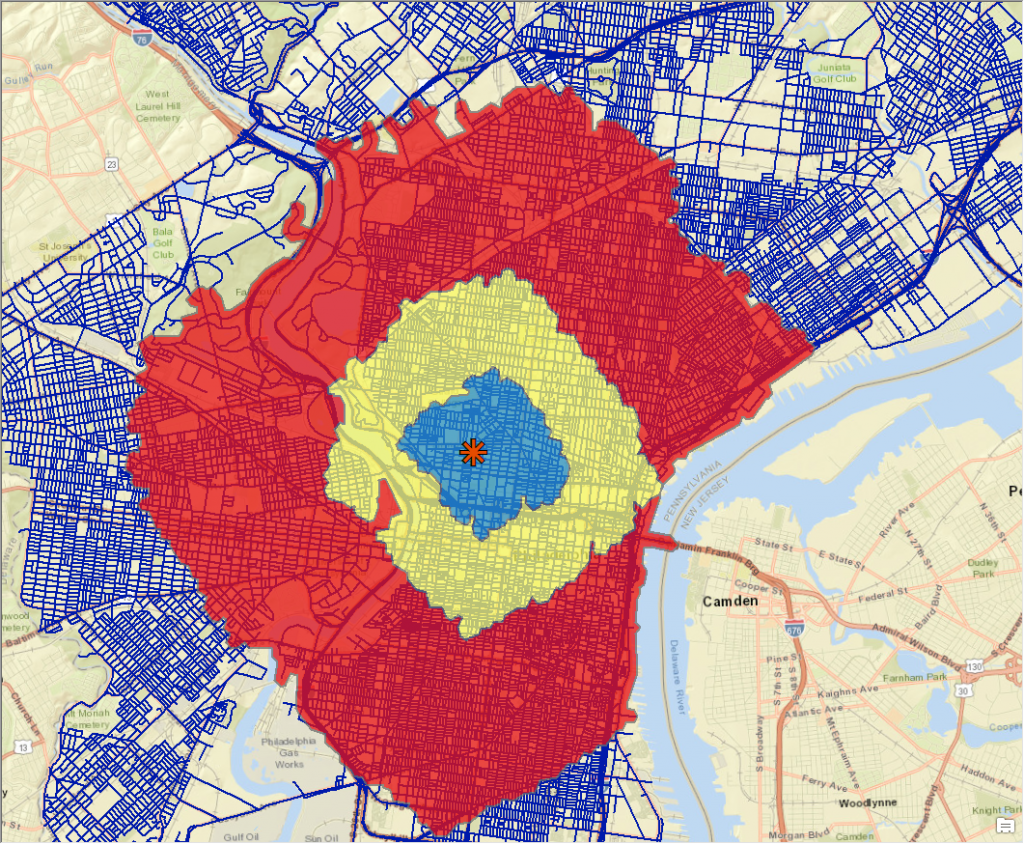
A Service Area Created Using Network Analyst

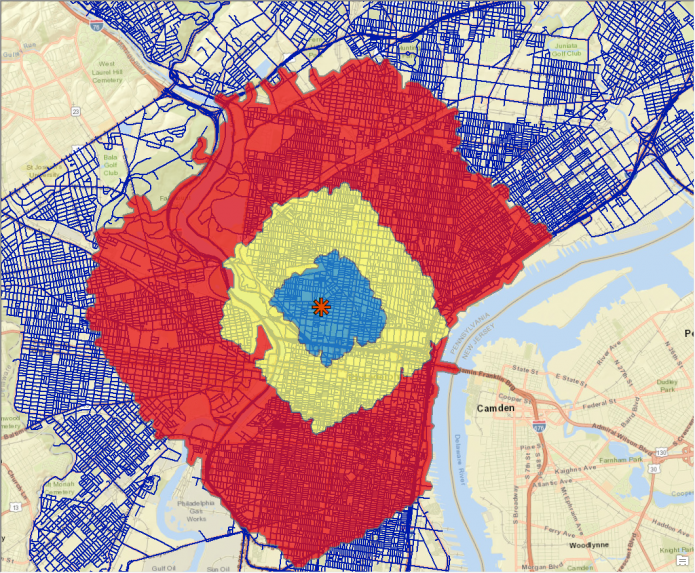
It looks very similar to a Euclidean buffer, except the most obvious difference is the uneven boundaries of each zone. I know you put in 1, 5, and 10 miles, but at first glance there seems to be more zone to the right of the POI in the 1 and 5 mile zones than to the left. Do you know how it is calculated?
Hey Josh, with the parameters used in the example above it is just determining how much ground can be covered (in miles) along the street network provided as opposed to the “as the crow flies” style euclidean buffer.
There are ways to incorporate speed and time into the analysis, which could drastically alter the output. But in this case, I think that the skew we are seeing is due to the lack of roads facing East-West in the Fairmount Park / Schuylkill River area.