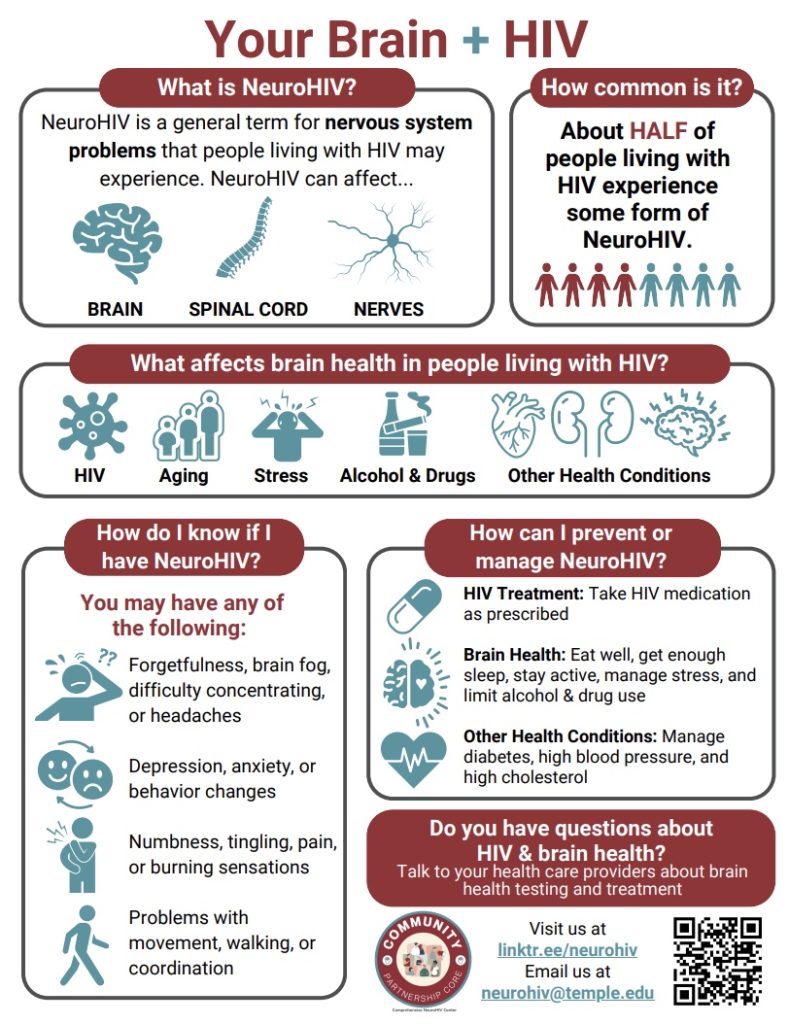
- NeuroHIV is a general term for nervous system problems that people living with HIV may experience.
- NeuroHIV can affect:
- The brain
- The spinal cord
- The nerves in your body
- About half of people living with HIV experience some form of NeuroHIV.
- The most common types of NeuroHIV are:
- Neuropathy: This usually involves numbness, tingling, pain, or burning sensations in the feet or hands. This is because of nerve damage.
- HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders (HAND): This involves problems with memory and thinking. This is because of HIV in the brain.
- Severe conditions like encephalitis and meningitis can also occur.
- These involve inflammation or infection in the brain and spinal cord.
- However, these conditions are rare, especially for those who are receiving regular HIV treatment.
- People with NeuroHIV may have any of the following:
- Forgetfulness, brain fog, difficulty concentrating, or headaches
- Depression, anxiety, loss of interest, or behavior changes
- Problems with movement, walking, or coordination
- Numbness, tingling, pain, or burning sensations
Not everyone with NeuroHIV will experience all of these symptoms.
- Many different things can affect brain and nerve health in people living with HIV. These include:
- The HIV virus: HIV can enter the brain and damage brain cells and nerves by releasing toxins.
- Inflammation: If the body’s immune system has been fighting HIV for a long time, it causes inflammation that can negatively impact the nervous system.
- Opportunistic infections: If an immune system is weakened by HIV infection, other infections have a greater impact on the body.
- Aging
- Stress
- Alcohol and drug use
- Other health conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
- HIV treatment: Take HIV medication as prescribed.
- Having an undetectable viral load can decrease the risk of NeuroHIV. An undetectable viral load means that HIV is not actively replicating or making new copies of itself.
- Brain health: Brain health can be supported by:
- Eating well (such as the Mediterranean diet)
- Getting enough sleep
- Exercising regularly
- Staying mentally and socially active
- Managing stress
- Limiting alcohol, tobacco, and drug use
- Other health conditions: Manage diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other health conditions.
- Talk to a health care provider about brain health testing and treatment. They may refer someone to:
- A neurologist: A doctor who can further assess and treat difficulties and prescribe medication.
- A neuropsychologist: A doctor who can assess memory and thinking problems in detail and offer recommendations.
- A physical therapist (PT), occupational therapist (OT), or speech therapist to help manage difficulties in daily life.
- If mental health support or resources are needed, consider talking to:
- A mental health professional: Psychiatrists, psychologists, or therapists can help manage depression and other mental health concerns.
- A social worker or case manager: These professionals can help connect someone with resources to manage NeuroHIV.