Research Overview
Renewable energy from biological feedstock is expected to play an important role in the global plan to replace petroleum-based fuels by sustainable alternatives, while reducing noxious and greenhouse gas emissions. Most bioenergy species currently used (e.g., maize, sugar cane, soybean) compete with land for food production.
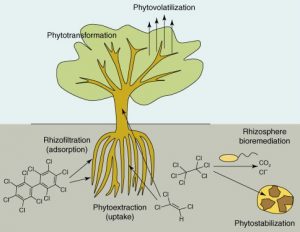
A promising sustainable alternative is to combine biofuel production with the rehabilitation of sites contaminated by toxic pollutants and unsuitable for edible crop cultivation. Lignocellulosic feedstock, such as switchgrass and poplar trees, efficiently remove toxic contaminants from soil (phytoremediation) and offer additional benefits, including the mitigation of atmospheric carbon dioxide, reduced soil erosion, and improvement of water quality and biodiversity.
Faculty Reseach
Van Aken research focuses on the use of soybean and switch grass plants for the phytoremediation of contaminated soil while generating feedstock for biodiesel and bioethanol conversion.
Technical Capabilities
– phytotechnology
– real-time PCR
– microarray
– RNA sequencing
– GC/MS, HPLC
– Autoclave, Class II Biosafety laminar flow.
Recent Publications
3. Changes in Arabidopsis thaliana gene expression in response to silver nanoparticles and silver ions.
R. Kaveh, Y-S Li, S. Ranjbar, R. Tehrani, C.L. Brueck, B. Van Aken
Environ Sci Technol (2013) ![]()
2. Uptake and metabolism of pharmaceuticals and other emerging contaminants by plants. In Phytotechnologies: Remediation of Environmental Contaminants.
B. Van Aken,R. Tehrani, R. Kaveh Naser AA, Pereira ME, Ahmad I, Duarte AC, Umar S, Khan NA (Eds.)
CRC Press, Boca Raton. pp 541-570 (2012) ![]()

Van Aken B, Correa PA, Schnoor JL
Environ Sci Technol. 44:2767-2776 (2010)
Return to Main